Germ is a common term for a large variety of microbial agents that can grow in or on people. Infection occurs when a germ usually causes a disease, although it is possible to have an infection without any symptoms of disease.
The germs that can cause infectious diseases in people include:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Parasites
- Fungi
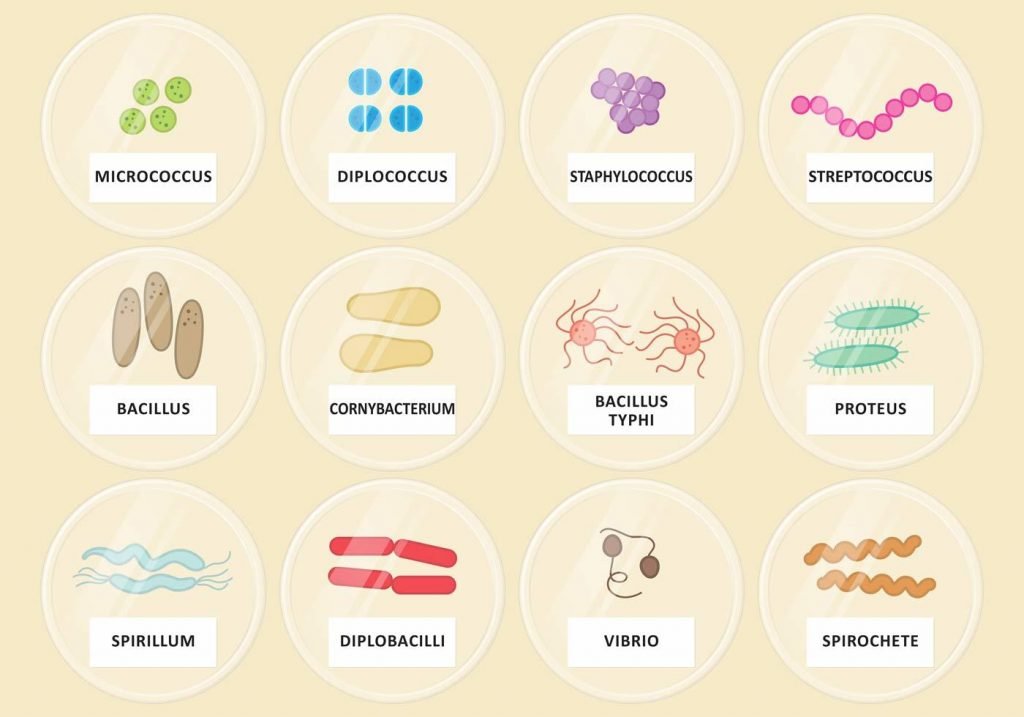
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that thrive in many different types of environments. They are extremely small, and they are everywhere. Some survive in extremely cold or heat environments. Others make their homes in people’s intestines, where they help digest food. Most bacteria cause no harm to people, but there are exceptions.
Infections caused by bacteria include tuberculosis and urinary tract infections. Inappropriate use of antibiotics has helped create strains of bacterial disease that are resistant to antibiotic treatments.
Viruses
Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and require living hosts, e.g. humans, plants or animals, to multiply. Otherwise, they cannot survive. When a virus enters our bodies, they invade some of our cells and takes over the cell machinery, redirecting it to produce the virus. They are very small and lightweight hence they can float through the air.
Some scientists argue that viruses are not alive as they cannot reproduce on their own and they do not metabolise food into energy, characteristics of a living thing. Diseases caused by viruses include chickenpox, measles, mumps, hepatitis and common colds.
Parasites
Parasitic infection or infestation can occur in children of all ages. Infants, toddlers, and very young children in daycare settings are at risk for the parasitic disease called giardiasis that causes diarrhoea and is spread through contaminated faeces. Pinworm infection (enterobiasis) also occurs among preschool and young school-age children. Both preschool and school-age children can become infested with head lice (pediculosis) or scabies, both of which are spread by close person-to-person contact as is common during childhood play.
Fungi
Fungal infections happen when fungi attack the outer layer of skin on the scalp or body. Some fungal infections need warm, moist, unclean skin to grow. This could lead to infection on skin, nails, and hair like oral thrush, candida diaper rash, tinea infections, etc. Encourage your child to adopt good hygiene practices to prevent fungal infections.
